

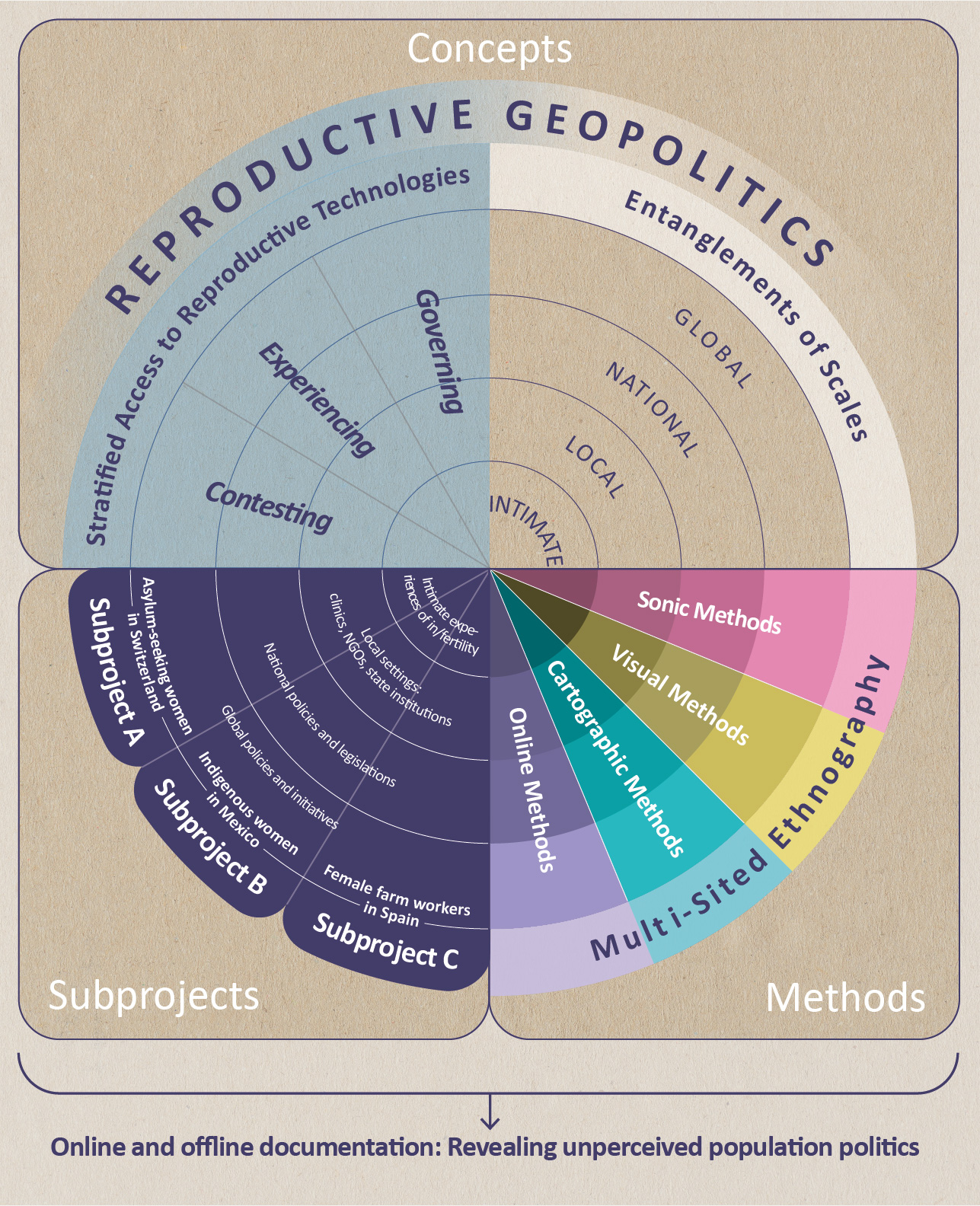















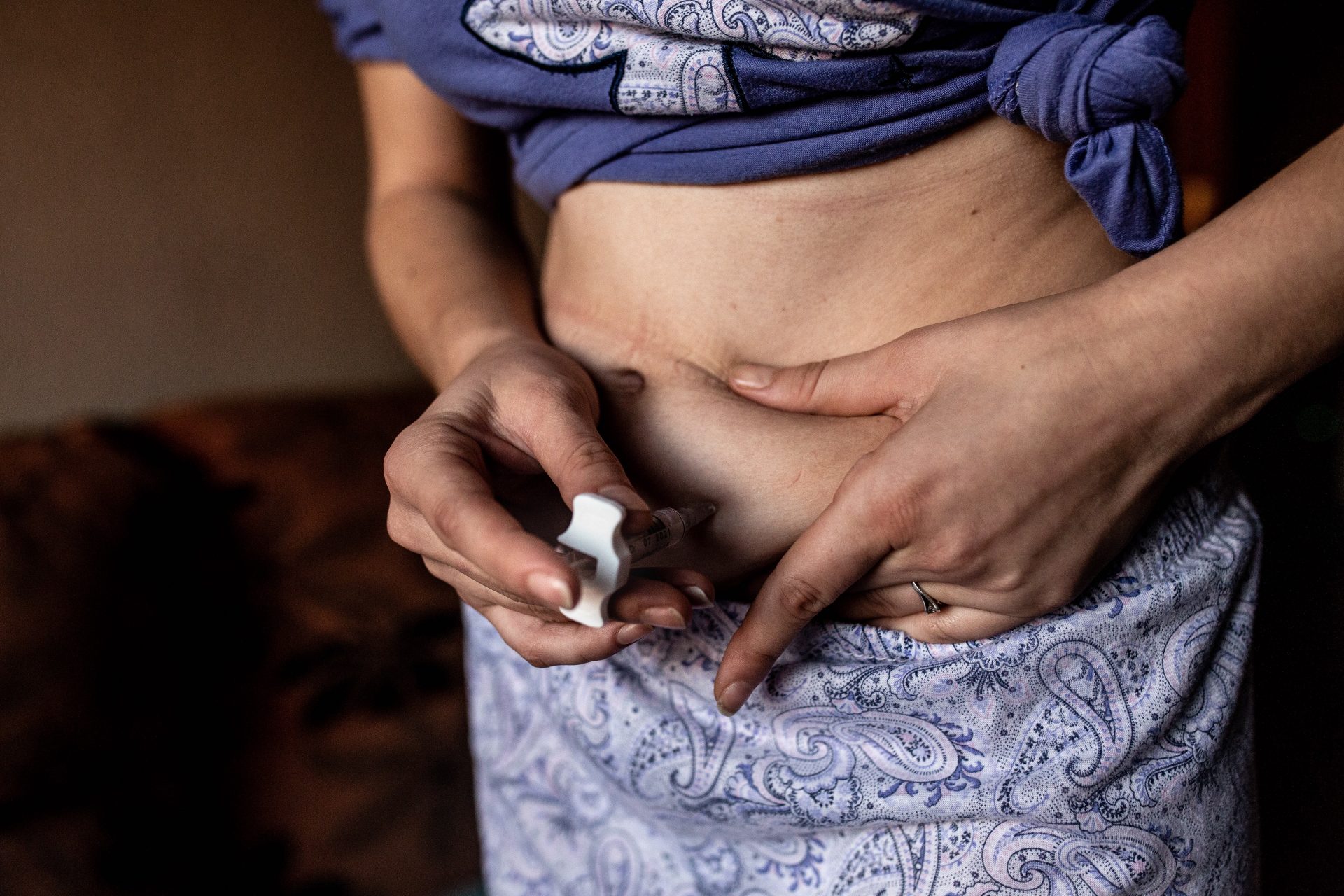





















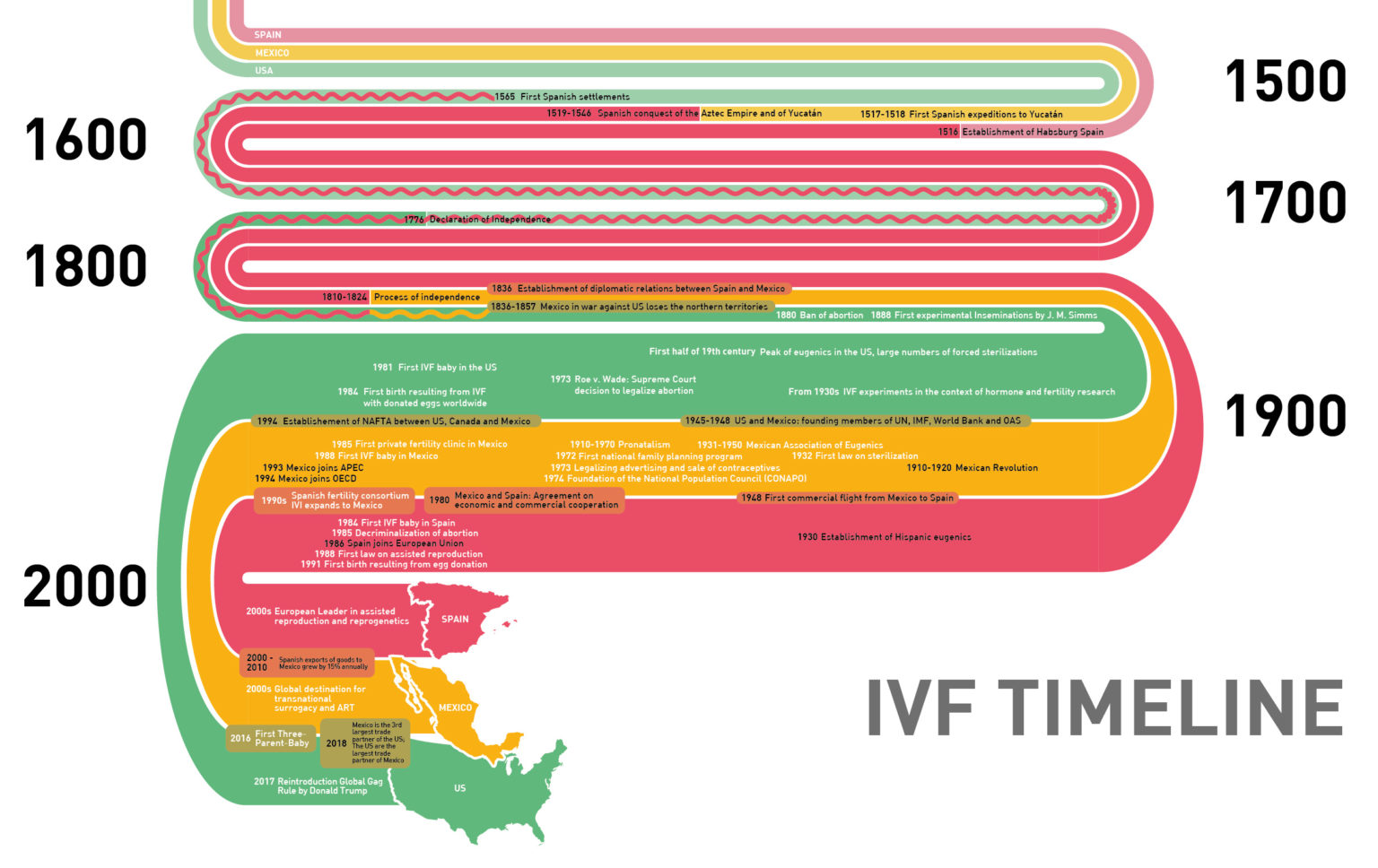









































Worldwide, more and more people are traveling abroad to fulfill their desire to have a child. In Switzerland, it is the relatively restrictive legal situation, especially compared to other European countries, and the high costs of reproductive procedures that encourage Swiss women to visit reproductive clinics abroad. The Swiss media often report on these new forms of transnational reproduction based on individual experiences, especially in the context of egg donation and surrogacy, but so far there are no figures on the extent of the phenomenon of transnational reproductive mobility in Switzerland. This commissioned study, conducted by the University of Bern on behalf of the Federal Office of Public Health BAG, uses quantitative social research methods to investigate how many Swiss residents traveled abroad in 2019, for what reasons, and for what reproductive procedures. The focus is on the following four procedures: in vitro fertilization (IVF), egg donation, sperm donation and surrogacy. The results are based on five different surveys addressed to physicians in Switzerland who are licensed to perform IVF procedures; reproductive medicine centers and sperm banks abroad; and selected cantonal supervisory authorities in the civil status service and Swiss consulates.
With the data collected as part of this study, information is available on 516 cases in which individuals or couples who resided in Switzerland in 2019 traveled abroad for a reproductive procedure. Most individuals were heterosexual couples (84.65%) and patients or intended parents between the ages of 35 and 44 (72.30%). By far the most frequently used procedure is egg donation, which accounted for 82.17% of all international trips and was performed mainly in Spain. The data presented in the study should be understood as an approximation of the quantitative extent of reproductive mobility. On the one hand, they are mainly based on estimates of the reproductive physicians, on the other hand, a high number of unreported cases must be assumed. However, an improvement of the data situation is central for an informed political discussion with regard to a possible change of the legal basis in Switzerland. For this purpose, reproductive medicine centers and germ cell banks in Switzerland and abroad would have to systematically keep anonymized statistics on their patients and clients and be willing to share them with scientists and authorities. Further qualitative research would also be important in order to develop a more differentiated view of the phenomenon of transnational reproductive mobility and the groups concerned and their experiences from Switzerland.